
The Importance Of Root Hair Cells
As a rule of thumb, most studies on root hair physiology have thus focused on the growing root hair tip, vastly neglecting any potential cell wall- or plasma membrane-forming cellular.
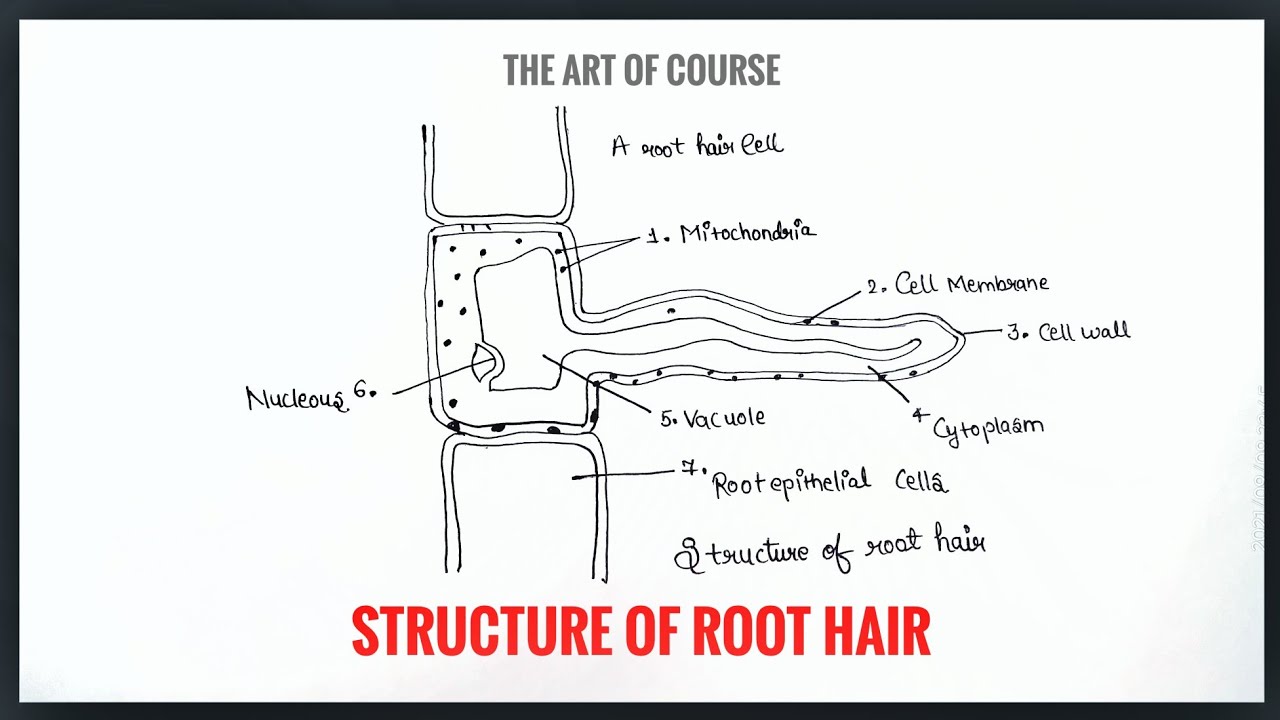
Structure of Root Hair Diagram with labelling theartofcourse YouTube
Background. The Arabidopsis root hair represents a valuable cell model for elucidating polar expansion mechanisms in plant cells and the overall biology of roots. The deposition and development of the cell wall is central to the root hair expansion apparatus. During this process, incorporation of specific wall polymers into the growing wall architecture constitutes a critical spatio-temporal.

Schematic of the human hair follicle. The hair follicle contains both... Download Scientific
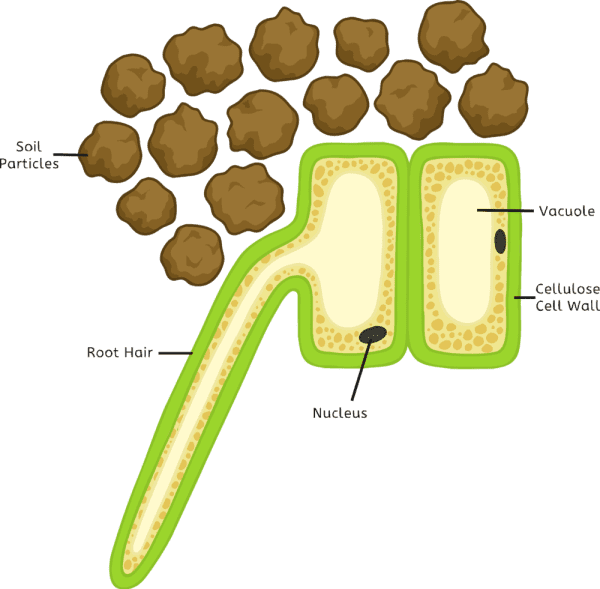
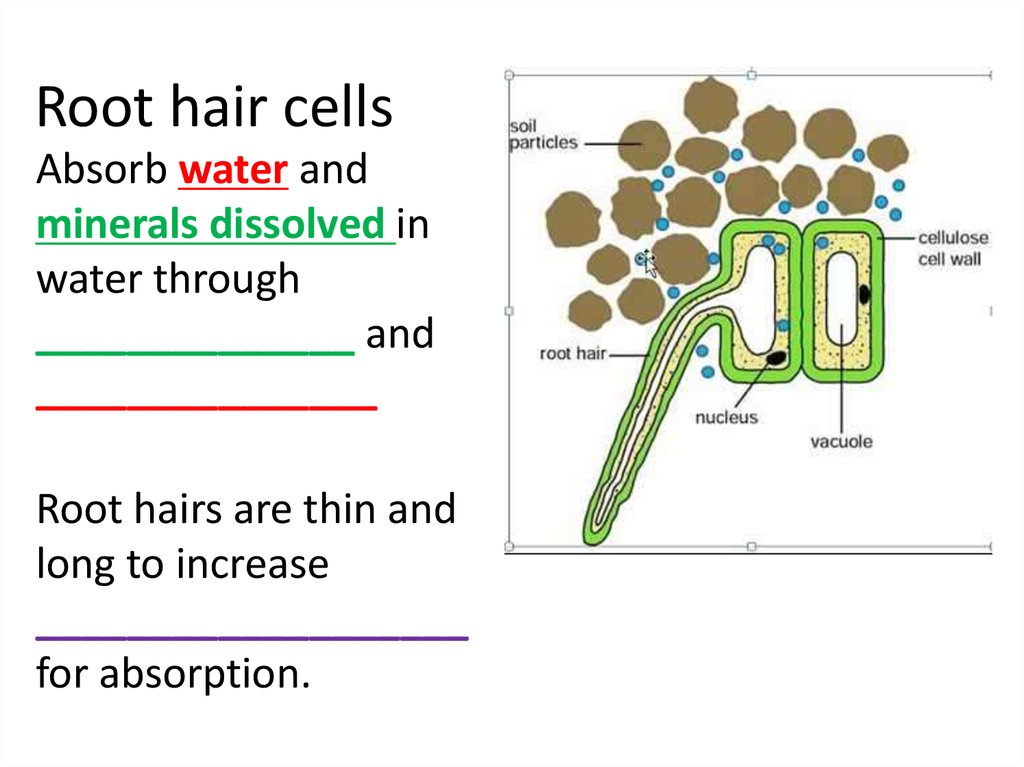
Root hair cells close root hair cell A specialised cell that increases the surface area of the root epidermis to improve the uptake of water and minerals. are adapted for taking up water and.
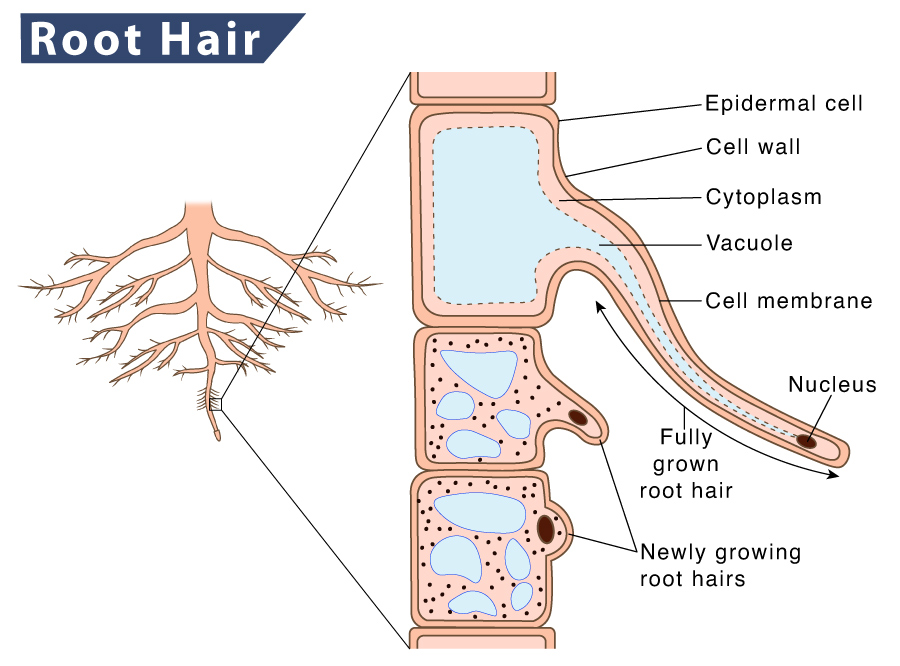
Active Transport In Root Hair Cells Of Plants Transport Informations Lane
Root Development . In plants, both roots and shoots grow from the tip or apex of the plant. New cells are produced in these growing tips by meristems, groups of undifferentiated cells whose function is to divide by mitosis to produce new cells.Root growth begins at the root apical meristem (RAM). This meristem divides in two directions, producing a root cap to the outside of the root to.
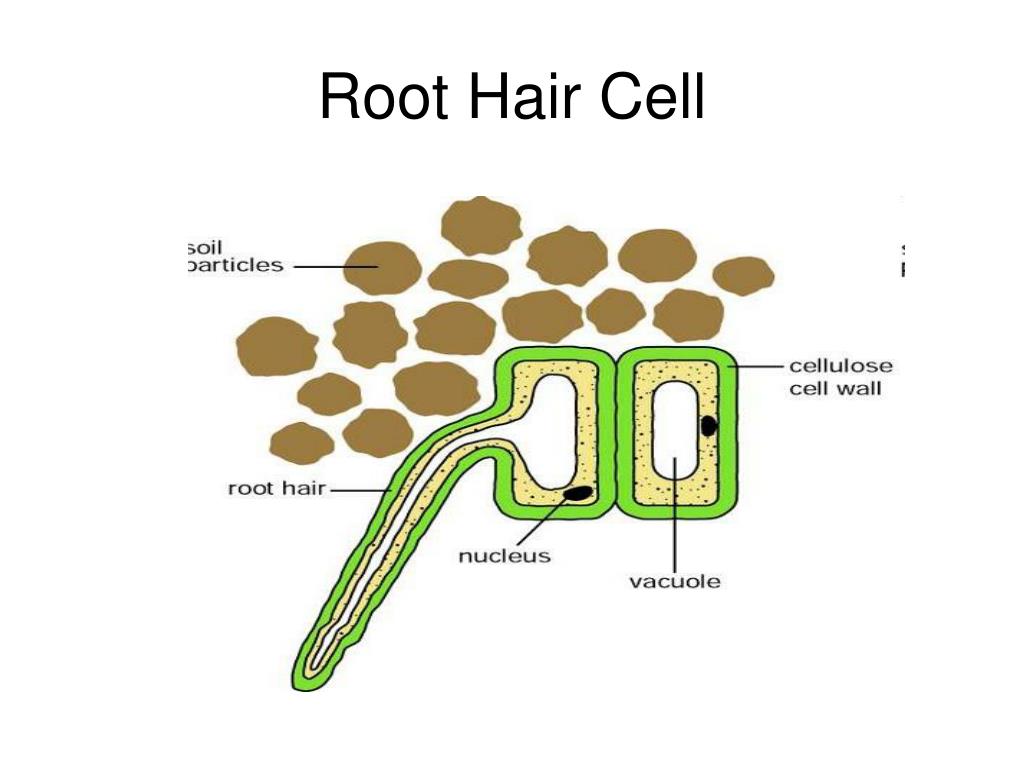
PPT Cell Types & Tissues PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1130552
The initial step in the formation of a root hair is the specification of a newlyformed epidermal cell to differentiate as a root hair cell. This represents an example of a central problem in developmental biology; namely, how do particular cell types acquire their identity?

Tammy Cannon News Roothaircellfromaplantfunction
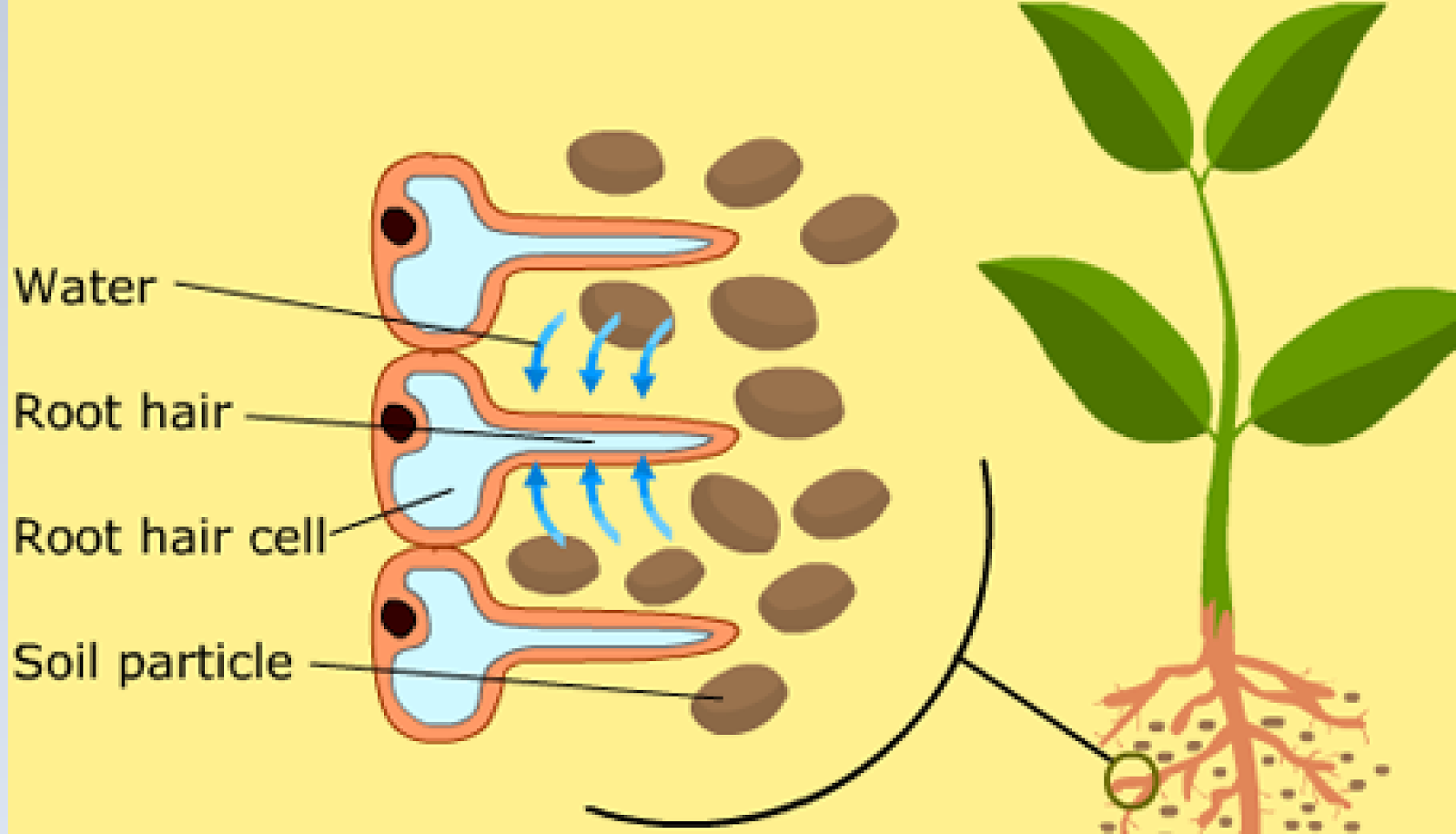
Water absorption occurs in root hairs. Root hair cells are present in the roots of the plants. Root hairs refer to the long and thin hairs that can penetrate between the soil particles. The larger surface area of the root hairs allows them to absorb water. Root hair cells are adapted to uptake water through osmosis and mineral ions through.
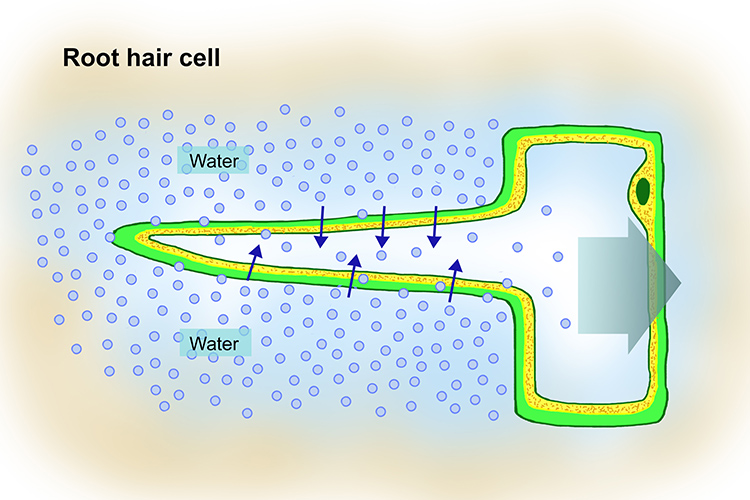
Root Hair Cells Diagram malayakram
Introduction Root hair cell is an offshoot of a hair-forming cell of the epidermis. It is mainly considered an exclusive feature of plants, but its contemporary is also found in animal species. The functional unit of root hair cells is recognized as" root hair."
Maturation Zone Of Root 5 5 The Root Biology Libretexts / Matured cells differentiate into
This lesson demonstrates and explains how substances (water and mineral salts) are absorbed by the root hair cells. Once you are doing photosynthesis and tra.

Root Hair Cell Biology
Why Root Hairs are an Excellent, Single-cell, Plant Model for Systems Biology? A root hair is a single cell ( Wan et al., 2005; Brechenmacher et al., 2009, 2012; Libault et al., 2010a; Qiao and Libault, 2013 ), structurally simple and tubular outgrowth of root epidermal cells ( Grierson et al., 2014 ).

Absorption Of Water
Live Arabidopsis root hairs may be labeled with cell wall polymer-specific antibodies. This methodology allows for direct visualization of cell wall dynamics throughout development in stable transgenic plant lines.
What are Xylem and Phloem? Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
Roots hairs are cylindrical extensions of root epidermal cells that are important for acquisition of nutrients, microbe interactions, and plant anchorage. The molecular mechanisms involved in the specification, differentiation, and physiology of root hairs in Arabidopsis are reviewed here.
Root Hair Cell Function Transport in Flowering Plants Root hair cell root hair cells are
A layer of cells known as the endodermis borders the stele (Figure 3.2.3. 2) and is considered the innermost layer of the cortex. The endodermis is exclusive to roots, and serves as a checkpoint for materials entering the root's vascular system. A waxy substance called suberin is present on the walls of the endodermal cells.
a2zPCMB root hair cells
The major regions of the root are labeled in the cross section above. The epidermis is the outermost layer of cells and includes elongated cells called root hairs. The cortex is the region of cells between the epidermis and the vascular tissue. The pith is the region of cells contained within the cylinder of vascular tissue.

Nutritional Requirements of Plants OpenStax Biology 2e
How are Diamonds Made Types of Meteorites Types of Volcanoes Types of Rocks Worksheets What is Root Hair hairs are tiny, unicellular, hairlike outgrowth present on the outer surface of roots. They extend from the outer layer of a called the epidermis. Root hairs are continually being sloughed off by the soil and regrown.

GCSE Biology Root Hair Cell Diagram Diagram Quizlet
Roots. Root systems and root hairs are adapted to play a special role in the plant. The root network spreads out to absorb water (and mineral salts) from a large amount of soil. It is also adapted to hold the plant firmly and provide support (anchor) to the plant in the soil. The role of root hairs in water absorption during photosynthesis.
.PNG)
Tammy Cannon News Roothaircellfromaplantfunction
In this system, the genesis of the root hair cell begins with two types of root epidermal cells: the H and N cells, which rapidly differentiate into root hair (trichoblasts) and hairless cells (atrichoblasts), respectively. Root hair determination and differentiation is cell position-dependent and is under the control of signal exchanges.